Brain Tumors: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Options
Receiving a diagnosis of a brain tumor—or even suspecting one—is an overwhelming experience. However, advancements in neuro-oncology and surgical technology have significantly improved outcomes and quality of life for patients.
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain. Some are noncancerous (benign), while others are cancerous (malignant). Regardless of the type, understanding the symptoms and the clinical pathway for diagnosis is the first step toward effective management.
Understanding Brain Tumors: Types and Classifications
Before diving into symptoms, it is essential to understand that not all brain tumors are created equal. They are generally categorized into two main groups:
- Primary Brain Tumors: These originate in the brain itself or in tissues close to it, such as the brain-covering membranes (meninges), cranial nerves, pituitary gland, or pineal gland.
- Secondary (Metastatic) Brain Tumors: These occur when cancer begins elsewhere in the body (such as the lungs, breast, or colon) and spreads to the brain. Metastatic tumors are far more common than primary tumors.
Furthermore, tumors are graded (Grade I to IV) based on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope and how quickly the tumor is likely to grow and spread.
Common Symptoms of a Brain Tumor
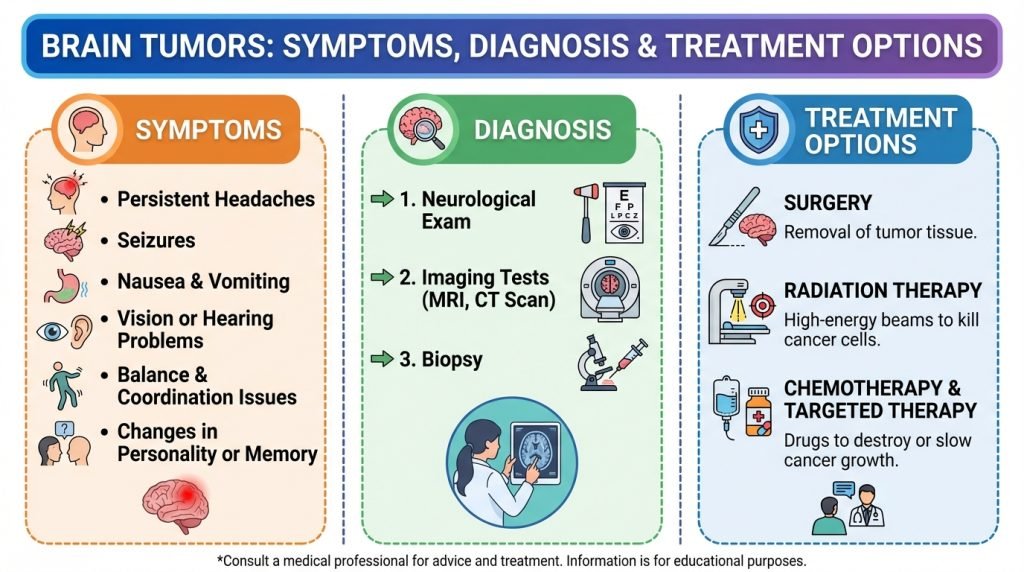
Symptoms of a brain tumor vary widely depending on the tumor’s size, growth rate, and location. Because the brain controls every bodily function, the “red flags” can be neurological, physical, or emotional.
1. New or Changing Headaches
While most headaches are not tumors, a brain tumor headache often has specific characteristics:
- They are often worse in the early morning.
- They may become more frequent and severe over time.
- They might be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
2. Seizures
Seizures are one of the most common signs of a brain tumor, even in people with no history of epilepsy. These can range from “grand mal” convulsions to subtle “absence seizures” where the person appears to stare into space.
3. Cognitive and Personality Changes
Tumors in the frontal lobe can cause shifts in personality, loss of inhibitions, or increased irritability. Patients may also experience:
- Memory loss or confusion.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- General “brain fog” that does not resolve.
4. Motor and Sensory Impairment
Depending on the location, a tumor may press on nerves that control movement:
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body (hemiparesis).
- Loss of balance or difficulty walking.
- Coordination issues (ataxia).
5. Vision and Hearing Changes
- Vision: Blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision (often caused by tumors near the optic nerve).
- Hearing: Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or hearing loss, particularly if it only affects one ear.
How are Brain Tumors Diagnosed?
If a brain tumor is suspected, a neurologist will perform a series of tests to confirm the presence, location, and type of growth.
The Neurological Exam
The doctor will test your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength, and reflexes. Difficulty in one or more areas provides clues about which part of the brain may be affected.
Imaging Tests (MRI and CT Scans)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The gold standard for brain tumor diagnosis. Functional MRI (fMRI) or Perfusion MRI may be used to see blood flow and identify active areas of the brain.
- CT Scan: Often used in emergency settings or if the patient cannot have an MRI. It provides a detailed cross-section of the brain structure.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the only definitive way to determine if a tumor is benign or malignant. A neurosurgeon removes a small sample of the tumor tissue, which is then analyzed by a pathologist to determine its grade and genetic makeup.
Current Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
Treatment plans are highly personalized based on the tumor’s type, size, and location, as well as the patient’s overall health.
1. Surgery (Craniotomy)
If the tumor is accessible, surgery is usually the first line of defense. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible (resection) without damaging vital brain tissue.
- Awake Brain Surgery: Sometimes performed when the tumor is near areas controlling speech or movement, allowing the surgeon to monitor brain function in real-time.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation uses high-energy beams (X-rays or protons) to kill tumor cells.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Gamma Knife): This is not “surgery” in the traditional sense. It uses multiple beams of radiation to give a highly focused dose of radiation treatment to a very small area.
- Proton Therapy: A newer type of radiation that uses protons instead of X-rays, potentially reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill tumor cells. While some chemo is taken orally or intravenously, one challenge is the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from chemicals. Specialized drugs or “wafers” (Gliadel wafers) placed during surgery are sometimes used to bypass this barrier.
4. Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted treatments focus on specific abnormalities within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. This is often used for specific types of high-grade gliomas.
5. Tumor Treating Fields (TTF)
This non-invasive therapy uses electric fields to disrupt the ability of cancer cells to divide. It involves wearing a device on the head and is often used alongside chemotherapy for glioblastoma patients.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from brain tumor treatment is a journey that extends beyond the hospital. Because the brain is highly plastic, many patients can regain lost functions through:
- Physical Therapy: To regain lost motor skills or muscle strength.
- Occupational Therapy: To help patients return to daily activities and work.
- Speech Therapy: Essential for those experiencing difficulty speaking or swallowing.